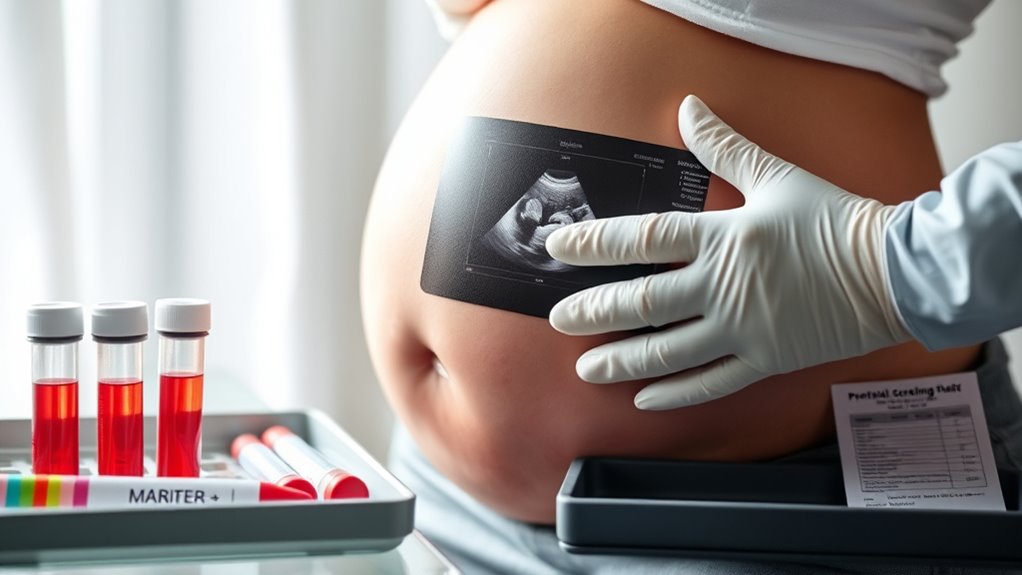
Prenatal screening tests, like blood tests and ultrasound markers, help you assess your baby’s health early on. Blood tests measure specific substances in your blood to estimate genetic risk, while ultrasound markers look for signs like nuchal translucency that might indicate concerns. These screenings aren’t diagnostic but provide valuable risk information, helping you make informed decisions. If you want to understand how these tests work and what they reveal, there’s more to uncover ahead.
Key Takeaways
- Prenatal screening includes blood tests and ultrasound markers to assess fetal health and genetic risks during pregnancy.
- Blood tests measure specific substances in maternal blood to estimate the likelihood of genetic conditions.
- Ultrasound markers, like nuchal translucency, detect physical signs associated with potential chromosomal abnormalities.
- Screening results indicate risk levels but do not provide definitive diagnoses; further diagnostic testing may be needed.
- Combining blood tests and ultrasound markers enhances screening accuracy and helps guide follow-up decisions.
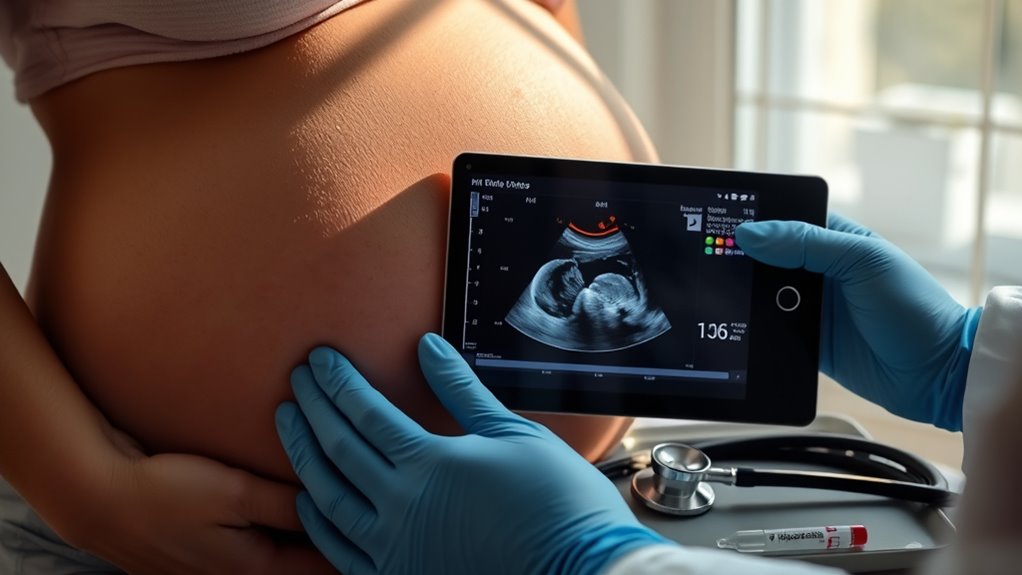
Prenatal screening tests are vital tools that help expectant parents and healthcare providers assess the health of your developing baby early in pregnancy. They provide valuable insights into potential genetic risks and help identify conditions that might need further testing or intervention. These screenings typically include blood tests and ultrasound markers, both of which work together to give a clearer picture of your baby’s health. Blood tests can measure specific substances in your blood that indicate the likelihood of certain genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome or trisomy 18. These tests don’t diagnose these conditions but estimate the risk, allowing you and your healthcare team to make informed decisions about next steps. Ultrasound markers, on the other hand, involve ultrasound scans that look for physical signs associated with genetic conditions. For example, certain markers like nuchal translucency (a fluid buildup at the back of the baby’s neck) can be linked to a higher chance of chromosomal abnormalities. Detecting these markers early helps determine whether additional testing is necessary, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling. Incorporating non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) can further refine risk assessments with high accuracy and minimal risk to the pregnancy.
When you undergo these screening tests, understanding the role of genetic risk is vital. These assessments analyze your baby’s likelihood of having specific genetic issues based on your age, family history, and the results of blood tests and ultrasound markers. If the risk appears elevated, your healthcare provider might recommend diagnostic tests that can confirm or rule out certain conditions with greater certainty. It’s important to recognize that a positive screening doesn’t mean your baby definitely has a condition—it’s simply an indicator that further testing is warranted. Conversely, a low-risk result can provide reassurance but doesn’t completely eliminate the chance of a problem. These screening tools are designed to give you a clearer sense of your baby’s health status without invasive procedures.
Ultrasound markers are particularly useful because they are non-invasive and can be performed early in pregnancy. They help detect physical features that might correlate with genetic abnormalities, providing additional context alongside blood test results. Combining these methods increases the accuracy of screening outcomes, giving you a more extensive understanding. Remember, these tests are part of a larger process aimed at supporting your pregnancy journey. They empower you to discuss potential concerns with your healthcare provider and plan appropriate care strategies. Ultimately, prenatal screening tests are about giving you information, peace of mind, and the opportunity to prepare for any necessary medical decisions or interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Prenatal Screening Tests Covered by Insurance?
Your insurance coverage for prenatal screening tests varies depending on your plan. Many insurance policies do cover these tests, but you should check with your provider to understand your specific cost considerations. Some plans may require co-pays or have limits on coverage. To avoid surprises, contact your insurance company early to confirm what’s covered and discuss any out-of-pocket expenses you might face.
How Early Can Blood Tests Detect Genetic Conditions?
Think of genetic screening as an early alarm clock that wakes you up to potential issues. Blood tests can detect genetic conditions as early as 10 weeks into pregnancy. This early detection gives you time to explore options and make informed decisions. These tests are designed to identify risks, not definitive diagnoses, but they’re invaluable for planning and peace of mind during your pregnancy journey.
Can Ultrasound Markers Predict All Types of Birth Defects?
Ultrasound markers can’t predict all birth defect types because of their limitations. While they can detect many structural issues, some defects, like certain genetic or metabolic conditions, may not show visible signs on ultrasound. You should understand these limitations and consult your healthcare provider for thorough testing options. Ultrasound is a valuable tool, but it doesn’t catch every birth defect, so additional screenings might be necessary.
What Are the Risks Associated With Prenatal Blood Tests?
You might face some risks with prenatal blood tests, such as false positives or negatives, which can cause unnecessary worry or missed diagnoses. There’s also a small chance of discomfort or bleeding from blood draws. Ultrasound concerns include potential anxiety from unclear results or unnecessary further testing. Overall, these tests are safe but it’s good to discuss any worries with your healthcare provider to understand the benefits and risks better.
How Accurate Are Ultrasound Markers in Diagnosing Chromosomal Abnormalities?
Ultrasound accuracy for diagnosing chromosomal abnormalities varies but generally provides a reliable screening tool. While ultrasound markers can suggest the likelihood of conditions like Down syndrome, they aren’t definitive. You should understand that ultrasound findings are part of a broader diagnostic process and often need confirmation through more precise tests. Trust your healthcare provider to interpret these markers correctly and guide you toward the most accurate chromosomal diagnosis.
Conclusion
Think of prenatal screening tests as your guiding stars, illuminating the path to your baby’s health. Blood tests and ultrasound markers are like gentle whispers from your growing little one, helping you catch potential concerns early. By understanding these tools, you’re crafting a clear map through the sky of pregnancy, ensuring you and your baby navigate this journey with confidence and hope. Trust these tests—they’re your compass in this beautiful adventure ahead.