Hormones in pregnancy trigger significant changes in your body and emotions. Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) supports early pregnancy, while progesterone and estrogen prepare your body for fetal development. You’ll notice mood swings due to these hormonal shifts, alongside physical transformations like skin glow and increased blood flow. As labor approaches, oxytocin and other hormones prepare you for childbirth. Understanding these changes can help you navigate your experience better, so there’s much more to discover.
Key Takeaways
- hCG maintains early pregnancy stages and prevents menstruation, ensuring the embryo’s survival.
- Progesterone thickens the uterine lining, reduces contractions, and can heighten emotional responses.
- Estrogen supports fetal development and prepares the body for labor as the pregnancy progresses.
- Oxytocin triggers uterine contractions during labor, while relaxin softens the cervix for childbirth.
- Hormonal fluctuations post-delivery can impact mood and recovery, highlighting the importance of emotional support.
Key Hormones and Their Roles in Pregnancy
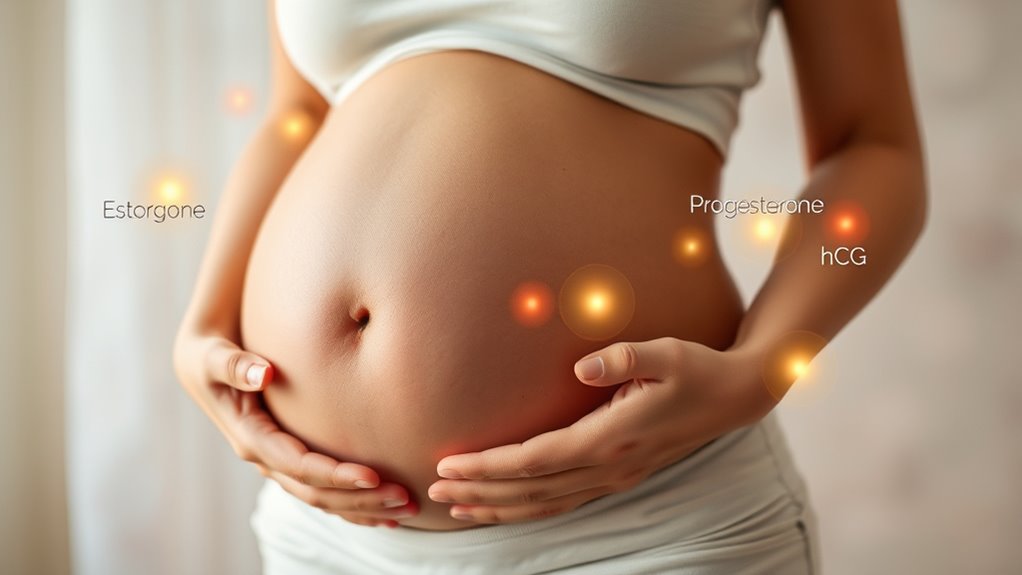

During pregnancy, key hormones play essential roles in supporting both the developing fetus and the mother’s body.
One of the most important is chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which your placenta produces to maintain the early stages of pregnancy. As hCG levels rise considerably in the first trimester, it signals your body to preserve the pregnancy.
Progesterone, secreted by both the ovaries and placenta, thickens your uterine lining, allowing for implantation and reducing uterine contractions. This process is crucial for long-term financial planning, as it ensures that the pregnancy is well-supported and healthy. Additionally, maintaining adequate levels of progesterone is essential for reducing the risk of complications during pregnancy.
Estrogen, produced by the ovaries and placenta, supports fetal development and prepares your body for labor.
Additionally, human placental lactogen (hPL) provides nutrition to your growing fetus and prepares your breasts for milk production, ensuring a healthy pregnancy for you and your baby. This hormonal balance is crucial for newborn feeding options, as it supports the overall health of both mother and child during this critical time.
Emotional Changes: Navigating Mood Swings

As your body undergoes significant hormonal changes during pregnancy, you may find yourself experiencing mood swings and emotional fluctuations. Increased levels of progesterone during the first trimester can amplify these feelings. To help stabilize your emotional well-being, consider incorporating regular exercise, like walking, which can boost endorphins and improve your mood. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding long gaps between meals can prevent hypoglycemia, which might worsen mood swings. Furthermore, engaging in nighttime meditation can further promote relaxation and emotional balance during this transformative time, as regular exercise has been shown to also positively influence hormonal levels. Incorporating mindfulness practices can also enhance your emotional resilience and help you navigate these changes more effectively.
Physical Transformations: What to Expect

Pregnancy brings a range of physical transformations that can be both surprising and exciting.
You’ll notice your skin may take on a radiant glow, thanks to the surge in hormones, particularly estrogen and the levels of progesterone. Increased blood flow enhances your complexion, but it can also lead to swelling and fluid retention, resulting in stretch marks for many women. To help manage these changes, consider using essential oils that are safe during pregnancy. Additionally, many women find that humor in texting can help lighten their mood during these transformative months.
Your body may feel different as ligament laxity increases, affecting your balance and stability. You might crave saltier or sweeter foods due to changes in taste preferences and heightened sensitivity to smells.
Additionally, hair growth patterns could shift, with some experiencing thicker hair while others face increased shedding. Nail brittleness or accelerated growth might also occur during this time. The focus on skin health is essential during pregnancy, as proper skincare routines can help manage these changes effectively.
Preparing for Labor: The Hormonal Shift
Understanding the hormonal shifts that occur as you approach labor is essential for guiding this transformative experience. Key hormones play important roles in preparing your body for childbirth:
- Oxytocin: This hormone increases markedly, stimulating uterine contractions and initiating labor.
- Relaxin: Produced by the placenta, relaxin softens the cervix and pelvic ligaments, making it easier for the baby to pass through the birth canal.
- Prostaglandins: These hormones aid in cervical ripening and enhance uterine contractions, critical for effective labor.
Additionally, an adrenaline surge during late labor provides you with energy and strength for delivery. Understanding the emotional volatility that may accompany this experience can help you better navigate the final stages of pregnancy and prepare for your baby’s arrival.
Postpartum Hormonal Adjustments

After childbirth, your body undergoes significant hormonal fluctuations that can affect both your mood and physical recovery.
You might notice mood swings and changes in energy levels as your hormone levels adjust.
Understanding these shifts can help you navigate this challenging yet transformative time.
Hormonal Fluctuations Explained
As you navigate the postpartum period, you’ll likely notice significant hormonal changes that can affect your mood and emotional well-being.
- After childbirth, progesterone and estrogen levels drop sharply, which may lead to mood swings.
- During breastfeeding, oxytocin levels rise, promoting milk production and strengthening your bond with your baby.
- Prolactin increases as well, primarily stimulating milk production, enhancing your caregiving instincts.
These hormonal fluctuations create a positive feedback loop, encouraging emotional attachment and nurturing behavior.
While low serotonin levels can contribute to feelings of sadness, most women experience mood stabilization around two weeks postpartum.
However, if you’re facing persistent emotional challenges, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional to rule out postpartum depression.
Impact on Mood
Hormonal adjustments in the postpartum period can substantially impact your mood. After childbirth, the significant drop in progesterone and estrogen can lead to mood swings and emotional instability.
You might find that low serotonin levels contribute to feelings of sadness or anxiety, but don’t worry—your mood typically stabilizes around two weeks after delivery.
However, keep in mind that postpartum depression affects 10-15% of new mothers, presenting persistent mood issues that may need medical evaluation.
Engaging in physical contact with your baby and breastfeeding can boost oxytocin, enhancing your emotional well-being.
If you’re struggling, consider reaching out to counseling or support groups; they offer valuable guidance and coping strategies during this challenging shift.
Physical Recovery Process
While your body undergoes significant changes postpartum, the recovery process is largely influenced by hormonal adjustments that promote healing and bonding.
After childbirth, your hormone levels fluctuate dramatically. Here are three key aspects of this process:
- Decreased progesterone and estrogen: These drops can affect your mood and emotional stability.
- Increased prolactin and oxytocin: These hormones boost milk production and enhance your connection with your baby.
- Skin-to-skin contact: This interaction fosters positive caregiving behaviors through hormonal feedback, aiding your recovery.
As you navigate this postpartum period, it’s crucial to be aware of these hormonal shifts, as they can contribute to mood changes and, in some cases, postpartum depression.
Support is critical during this time.
The Importance of Support and Healthy Habits

Support and healthy habits are vital during pregnancy, as they can greatly influence your emotional and physical well-being.
For pregnant women, maintaining a balanced diet is important; it stabilizes mood and helps manage hormonal fluctuations. Eating nutrient-rich foods regularly prevents hypoglycemia, keeping your mood steady.
Incorporating light exercise, like walking, can release endorphins that boost your mood. Staying connected with healthcare providers guarantees you have access to support and resources for managing emotional changes.
Engaging in antenatal courses not only equips you with valuable knowledge about childbirth but also helps you bond with other expectant mothers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Hormonal Changes During Pregnancy?
During pregnancy, you’ll experience significant hormonal changes that play crucial roles.
Estrogen and progesterone levels rise, helping maintain the uterine lining and preventing contractions. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) peaks in the first trimester, signaling pregnancy.
You’ll also see an increase in Human Placental Lactogen (hPL), which supports fetal nutrition and prepares your breasts for breastfeeding.
Relaxin levels rise too, easing ligaments and muscles to accommodate your growing baby.
What Changes Occur During Pregnancy?
As you commence this incredible journey, you’ll notice several changes happening within your body.
Your heart may race as blood volume increases, while your skin might glow or change.
You might experience cravings or aversions, and fatigue could become your new companion.
Your body’s preparing to nurture life, adjusting to accommodate the growing fetus.
Embrace these transformations; they’re signs of the miraculous process unfolding inside you.
Each change brings you closer to welcoming your little one.
What Are 5 Warning Signs of a Possible Problem During Pregnancy?
During pregnancy, it’s essential to watch for warning signs that could indicate a problem.
If you experience severe abdominal pain with bleeding, seek immediate help.
Persistent headaches that don’t respond to medication might signal high blood pressure.
Notice sudden swelling in your hands or face? That could be preeclampsia.
A drop in fetal movement after 28 weeks should prompt a call to your doctor.
Finally, don’t ignore severe shortness of breath or chest pain.
What Happens to the Levels of Estrogen and Progesterone During Pregnancy?
You might think hormones only affect mood, but their role in pregnancy is essential.
During pregnancy, estrogen and progesterone levels rise considerably. Estrogen, primarily from the placenta, supports fetal development, while progesterone thickens the uterine lining and prevents contractions.
These hormonal changes lead to various physical and emotional shifts, including mood swings and nausea. As pregnancy progresses, estrogen peaks to prepare for labor, while progesterone helps maintain the environment until birth.
Conclusion
As you navigate the incredible journey of pregnancy, remember that your body’s hormonal shifts are both powerful and transformative. Embrace the mood swings and physical changes, knowing they’re part of the beautiful chaos of bringing new life into the world—like a butterfly emerging from its chrysalis. After childbirth, be gentle with yourself during hormonal adjustments, and lean on your support network. By prioritizing healthy habits, you’ll not only thrive but also nurture your little one from day one.









