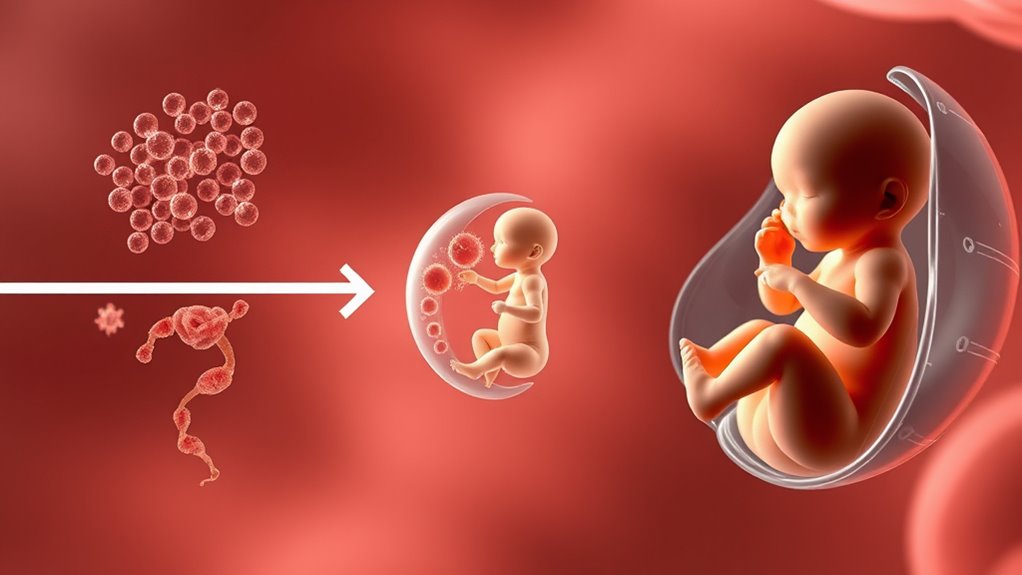
Fetal development occurs in three main stages: germinal, embryonic, and fetal. In the germinal stage, which lasts about two weeks, rapid cell division happens as the fertilized egg attaches to the uterus. Next, during the embryonic stage, critical organs and structures form. Finally, in the fetal stage, the baby grows and matures until birth. Understanding these stages helps you see how a tiny cell becomes a fully developed baby—you’ll discover more if you keep exploring.
Key Takeaways
- The germinal stage lasts about two weeks, involving fertilization, cell division, and implantation into the uterine lining.
- The embryonic stage follows, where major organs and structures begin developing during weeks 3-8.
- The fetal stage spans from week 9 until birth, characterized by growth and maturation of organs and tissues.
- Proper maternal nutrition and health are crucial throughout all stages for healthy fetal development.
- Each stage builds upon the previous, requiring careful nurturing to ensure successful progression to full term.
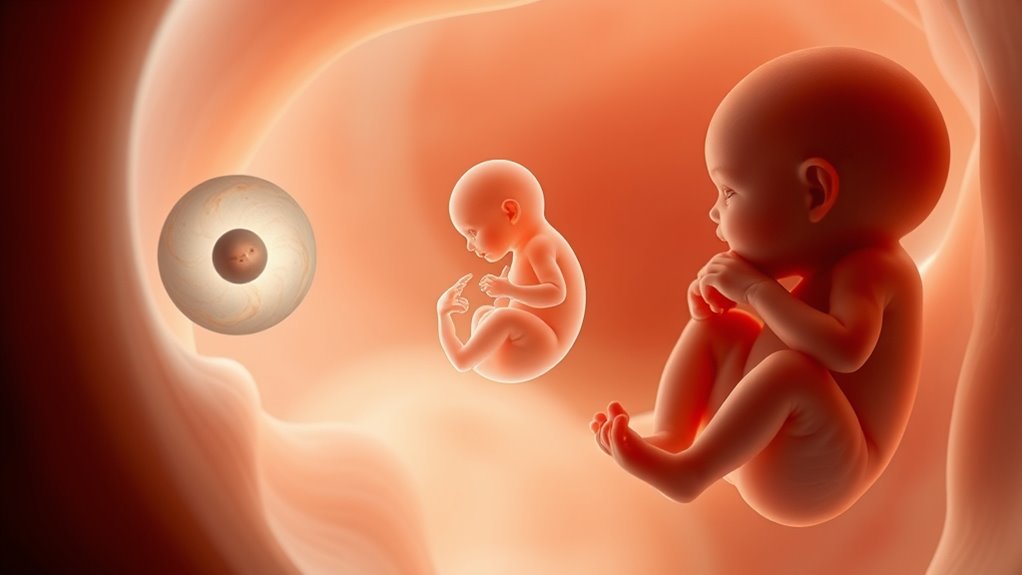
Fetal development is a remarkable process that unfolds over approximately nine months, transforming a fertilized egg into a fully formed baby. During this time, your body plays a vital role in supporting this journey, especially through prenatal nutrition and maternal health. What you eat and how you care for yourself directly influence how your baby develops at every stage. From the moment of conception, your body provides the building blocks necessary for growth, making proper nutrition essential. Nutrients like folic acid, iron, calcium, and vitamins ensure your baby’s organs, bones, and tissues develop correctly. Maintaining good maternal health, including regular check-ups and managing stress, creates the optimal environment for your baby’s growth and reduces the risk of complications. Retirement Planning resources and strategies can serve as an analogy for how careful planning and nurturing are essential for successful development.
Prenatal nutrition and maternal health are vital for healthy fetal development throughout pregnancy.
In the germinal stage, which lasts about two weeks after conception, rapid cell division occurs. During this phase, the fertilized egg travels down your fallopian tube and attaches to your uterus lining. While this stage is brief, it sets the foundation for all subsequent development. Proper prenatal nutrition during this phase is crucial, as deficiencies can impact implantation and early cell formation. Maternal health factors like avoiding harmful substances and managing pre-existing conditions help ensure this early process proceeds smoothly. Even in these initial weeks, your body’s health influences how well the embryo will develop, highlighting the importance of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Tell Which Stage My Pregnancy Is In?
You can tell which stage your pregnancy is in by tracking your ultrasound timing and using pregnancy tracking apps or charts. Typically, ultrasounds around 6-12 weeks help confirm early stages, while later scans show fetal development progress. By noting your last period date and scheduling ultrasounds accordingly, you’ll get a clearer picture of your pregnancy stage, helping you stay informed and prepared throughout your journey.
Are There Any Specific Risks During Each Development Stage?
You might worry about risks during pregnancy, but knowing that genetic mutations and maternal health influence each stage can ease your mind. During early development, genetic mutations may increase miscarriage risk, especially if maternal health isn’t ideal. Later, issues like preterm labor or fetal growth problems could arise. Staying healthy, attending regular checkups, and avoiding harmful substances help minimize these risks at every stage, ensuring better outcomes for you and your baby.
How Do Fetal Development Stages Vary Across Different Pregnancies?
You’ll notice that fetal development stages can vary across pregnancies due to genetic factors and environmental influences. These factors might affect growth rates, organ development, or susceptibility to complications. For example, genetic differences can lead to variations in size or development timing, while environmental factors like nutrition or exposure to toxins can impact each stage. Being aware of these influences helps you understand why no two pregnancies are exactly alike.
Can Certain Behaviors Affect Fetal Development at Each Stage?
Your behaviors can markedly impact fetal development at each stage. For example, during early stages, substance use or stress may cause developmental issues, while poor nutrition affects growth later. Environmental factors like exposure to toxins or high stress levels can hinder proper development throughout pregnancy. Staying healthy, avoiding harmful substances, and managing stress are essential to support your baby’s growth and reduce risks at every stage.
What Are the Most Common Developmental Abnormalities During These Stages?
Did you know about 3-4% of newborns have congenital anomalies? During development, you might encounter genetic anomalies and structural defects, which are the most common abnormalities. These issues can occur at any stage due to genetic mutations or environmental factors. You can reduce risks by avoiding harmful substances and maintaining good health. Early detection and intervention are vital for managing these developmental abnormalities effectively.
Conclusion
As you imagine this tiny miracle growing inside, each stage paints a vivid picture of life’s delicate yet resilient dance. From the spark of conception to the intricate formation of organs and the gentle swell of a future heartbeat, you witness nature’s masterpiece unfolding. Remember, within this tiny universe, hope and potential bloom silently, reminding you that every beginning holds a world of possibility waiting to blossom into something extraordinary.